A long put is a term used when you own a put option for an underlying asset. A put option is a contract where the buyer of the put has the right (not the obligation) to exercise a sell transaction at a specific strike price before an expiration date.
In the world of trading, owning a long put means that you have a contract that gives you the right to sell the underlying asset at a specific price, before a maturity date. Once the contract is exercised, the contract disappears and the underlying asset will be sold at the specified strike price. If you already have the asset in your open positions, it will be sold at the specified price. If you do not own the asset, the sell action will be expressed as if you have shorted the stock. The alternative of exercising would be to sell your contract to another trader on the market.
What are its components? Can you show me how to long a put option?
The components of a long put are quite simple. You simply need to perform an order to buy to open an option contract based on your desired specifications:
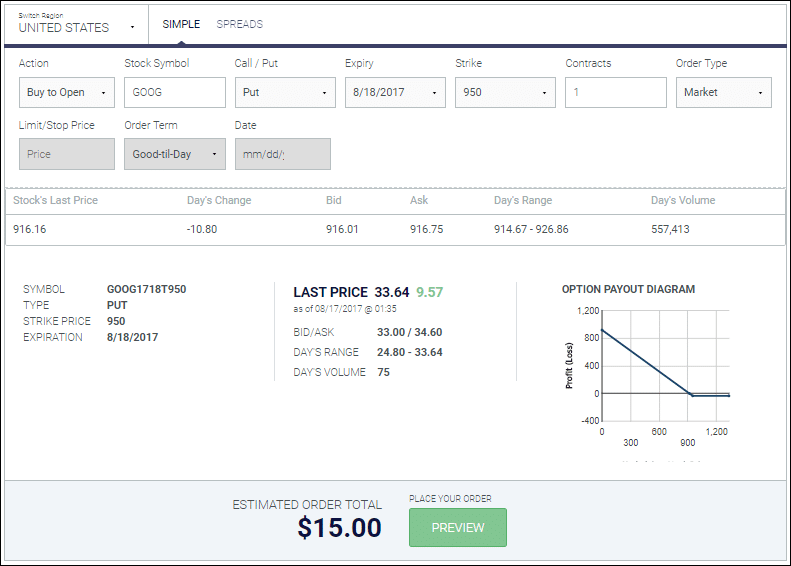
When and why should I have a long put?
You should have a long put option if you expect the stock price to go below a specific price, but would also like to have a cushion of protection. As an example, if you short sell the underlying asset and the price goes up, the loss will have a stronger impact on the underlying asset than on the contract.
What does it look like graphically? What is the payoff and profit graph?
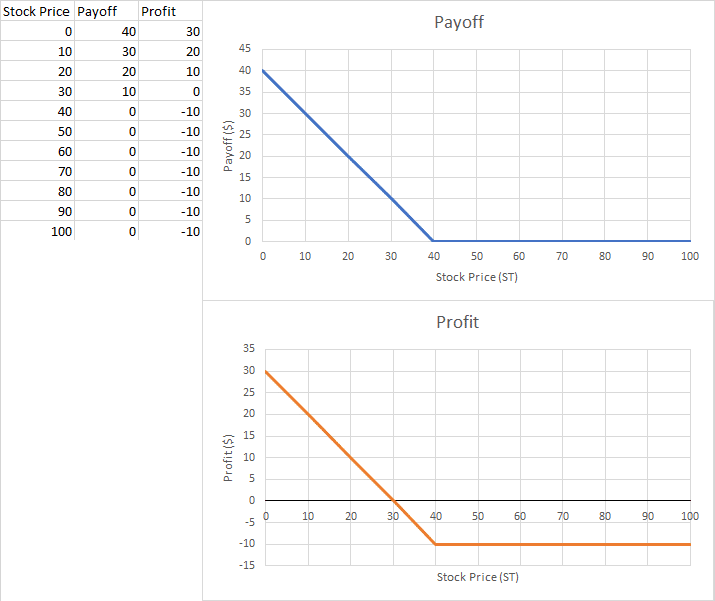
What is the break-even point?