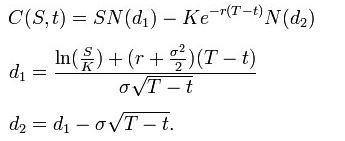Any discussion of options and option prices would be incomplete without a mention of the Black-Scholes The most generally accepted option pricing model. option pricing model.
Any discussion of options and option prices would be incomplete without a mention of the Black-Scholes The most generally accepted option pricing model. option pricing model.
Academics Fischer Black and Myron Scholes, in a paper they authored in 1973, stated their theory that an option was implicit to the pricing of any traded security.
Referencing the work of some of the most famous economists, like Paul Samuelson, Black and Scholes developed not one, but three “positions” for your consideration.
- The Black-Scholes Model: A mathematical calculation regarding equities (stocks).
- The Black-Scholes PDE (Partial Differential Equation): This tracks a certain stock’s motion or movement.
- The Black-Scholes Formula: This attempts to compute the prices for put and call options The right, but not the obligation, to buy a stock at a certain price before the expiration date. .
Unless you are a dedicated and hopeless mathematician, you need only know how the work of Black-Scholes might affect your investment activities. While many experts state the limitations of this theory, you might adopt the predictions and projections offered by Black-Scholes calculations to help your options activity.
The Black Scholes formula is used for obtaining the price of European put and call options. It is obtained by solving the Black–Scholes PDE – see derivation below.
Using this formula, the value of a call option in terms of the Black–Scholes parameters is:
The price of a put options The right, but not the obligation, to sell a stock at a certain price before the expiration date. is:
![]()
For both, as above:
- N(•) is the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution
- T – t is the time to maturity
- S is the spot price of the underlying asset
- K is the strike price The price at which the option contract can be executed.
- r is the risk free rate (annual rate, expressed in terms of continuous compounding)
- σ is the volatility in the log-returns of the underlying
All you need to know is that many option trading websites will now show you the Black-Scholes pricing calculation so you can gain a sense of the reasonableness of the option price.