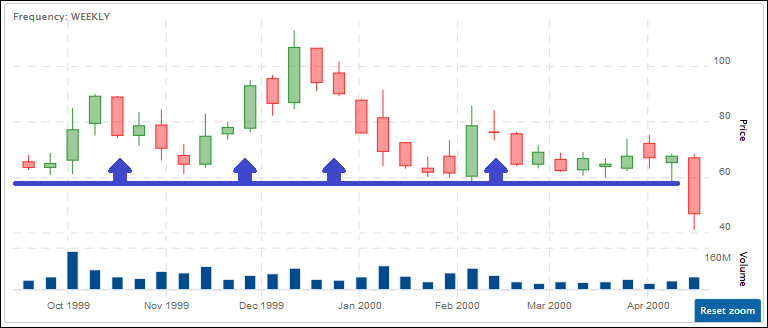
A Trading Halt is the temporary suspension of trading of a security for a specific period of time. Trading Halts typically last for an hour, but can extend into days.
Time Decay is the inclination for options to decrease in worth as the expiration date draws near. The extent of the time decay is inversely connected to the changeability of that option.
The Sharpe Ratio looks at a portfolio’s return over time, then gives it a rating based on how volatile the returns are. Portfolios with steady returns have a better Sharpe Ratio than portfolios with high returns but big swings
Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) is a method used by investors to prioritize what stocks to invest in, given their limited cash.
The basic form of short selling is selling stock that you borrow from an owner and do not own yourself. In essence, you deliver the borrowed shares. Another form is to sell stock that you do not own and are not borrowing from someone. Here you owe the shorted shares to the buyer but “fail to deliver.”
The cash received from the short sale of a security. The interest return from investment of the short proceeds is usually divided between the short seller, who gets partial “use of proceeds,” and the securities lender.
Short selling is the act of borrowing a security from someone else, usually a broker, selling it and later repurchasing the stock in the hopes that it will be cheaper.
Buying on margin is borrowing money from a broker to purchase stock.
Cash Flow Per Share is a ratio of the cash generated divided by the number of outstanding shares.
Form 10-Q, is also known as a 10-Q or 10Q, is a quarterly report mandated by the United States federal Securities and Exchange Commission, to be filed by publicly traded corporations.
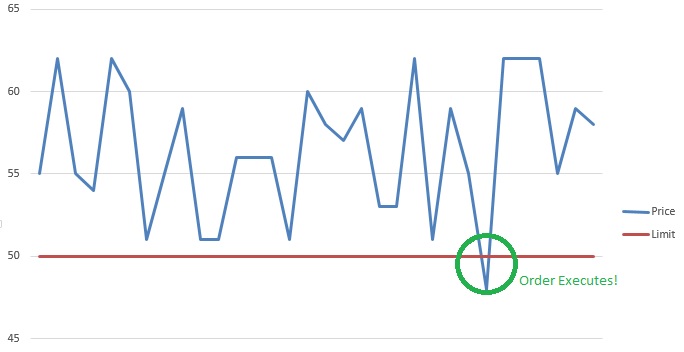
A Stop Loss Order is placed with a broker to sell a security when it reaches a certain price. A stop-loss order is designed to limit an investor’s loss on a security position.
A Stop Order is an order to buy or sell a stock when the stock price reaches a specified price, which is known as a stop price. When the specified price is reached, the stop order becomes a market order.
A limit order is an order to buy or sell a stock at a specific price or better. A buy limit order can only be executed at the limit price or lower, and a sell limit order can only be executed at the limit price or higher. A limit order is not guaranteed to execute. A limit order can only be filled if the stock’s market price reaches the limit price.
A market order is an order to buy or sell a stock at the best available price. Generally, this type of order will be executed immediately. However, the price at which a market order will be executed is not guaranteed. It is important for investors to remember that the last-traded price is not necessarily the price at which a market order will be executed. In fast-moving markets, the price at which a market order will execute often deviates from the last-traded price or “real time” quote.
The price, aka “the ask”, is the lowest price that a seller is willing to accept for a security.
When you are selling your shares of a security, the bid price is what the buyer is willing to pay for your shares.
A Dividend Yield is a financial ratio that shows how much a company pays out in dividends each year relative to its share price. In the absence of any capital gains, the dividend yield is the return on investment for a stock. The formula is Annual Dividends Per Share divided by Price Per Share.
Dividends are payments made by a corporation to its shareholder members. It is the portion of corporate profits paid out to stockholders. When a corporation earns a profit or surplus, that money can be put to two uses: it can either be re-invested in the business (called retained earnings), or it can be distributed to shareholders. There are two ways to distribute cash to shareholders: share repurchases or dividends. Many corporations retain a portion of their earnings and pay the remainder as a dividend.
Preferred stock is a special class of stock issued by a company that pays dividends. Preferred stock is more like a bond than true stock because the main appeal is dividend income. Most preferred stocks are limited in the total profit they can earn.
Common stock is a form of corporate equity ownership, a type of security. The terms “voting share” or “ordinary share” are also used in other parts of the world; common stock being primarily used in the United States. It is called “common” to distinguish it from preferred stock.
By law, every year, mutual funds must distribute that year’s net investment income (the total of dividends and interest received, less fund expenses) and net realized gain (gains less losses on securities sales) to its shareholders.
Profit or loss resulting from the sale of certain assets classified under the federal income tax legislation as capital assets. This includes stocks and other investments such as investment property.
A Call Option gives the holder the right, but not the need to purchase a fixed quantity of a particular stock at a specific price inside a particular time. Call Options are bought by investors who anticipate a price increase.
Blue Chip Stocks are from leading and nationally known companies that offer a record of continuous dividend payments and other strong investment qualities.
Block trades are greater than or equal to 10,000 shares in size and greater than or equal to $100,000 in value!
Beta measures a stock’s volatility versus the market’s volatility. Read this article to learn more and see an example of Beta.
The tendency of the stock market to trend higher over time. It can be used to describe either the market as a whole or specific sectors and securities.
A Bear Market is a long period where the stock market value falls along with a sense of pessimism for the public. Read this article to learn more!
At The Money refers to an option whose strike price equals the price of the underlying equity, index or commodity.
An all-or-none order is an order type that only executes when the full amount of the shares in the order can be executed.
Technical Analysis is the use of technical indicators comprising of statistics using past market information to predict which direction the security price will move. Read this post to learn about the 6 principles that formed the foundation of technical analysis, and some of its purposes and uses.
Trailing Stop is a Stop Loss order which is placed as a percentage value as opposed to an absolute dollar value. The order will only execute if the price of the security falls by a certain percentage.
Margin is the amount of money supplied by an investor as a portion of the total funds needed to buy or sell a security, with the balance of required funds loaned to the investor by a broker, dealer, or other lender.
Current Ratio is the ratio of current assets divided by current liabilities. It provides A liquidity ratio that measures a company’s ability to pay short-term obligations. Also known as “liquidity ratio”, “cash asset ratio” and “cash ratio”.
Buy-Side Firms are institutions that provide advice on buying securities and assets within their own organizations.
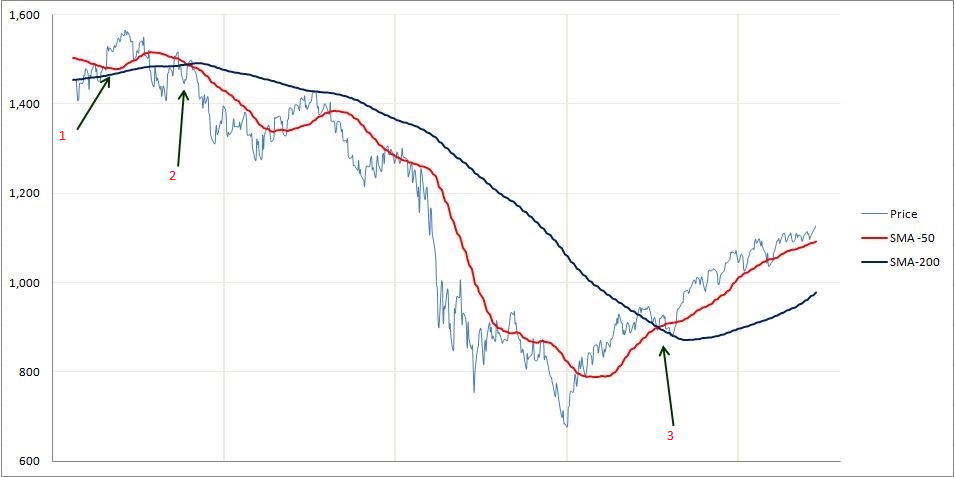
In simple terms, the moving average is an average that compares the previous period over time. There are two types of moving averages: the Simple Moving Average (SMA) and the Exponential Moving Average (EMA) which puts more weight on the latest date.
A dollar Trailing Stop is a Stop Loss order which is placed as a dollar value. The order will only execute if the price of the security falls by that dollar amount.
A zero coupon bond is a bond sold without interest-paying coupons. Instead of paying periodic interest, the bond is sold at a discount and pays its entire face amount upon maturity, which is usually a one year period or longer.
Yield To Maturity is the interest rate that will make the present value of a bond’s remaining cash flows (if held to maturity) equal to the price (plus accrued interest, if any).
Yield is the return investors can expect on a security based on all the outflows and inflows they incur related to that security.
Volume is the quantity of shares/contracts of a security that is traded within a specific time period.
Unsystematic Risk is the risk that is unique to a company such as a strike, the outcome of unfavorable litigation, or a catastrophe that affects its production.
Treasury bills, often referred to as T-bills, are short-term securities (maturities of less than one year) offered and guaranteed by the federal government. They are issued at a discount and pay their full face value at maturity.
A percentage Trailing Stop is a Stop Loss order which is placed as a percentage value as opposed to an absolute dollar value. The order will only execute if the price of the security falls by a certain percentage.
Tick refers to a change in price, either up or down.
Strike Price is the price at which an option can be exercised to buy or sell the underlying stock or futures contract.
S&P 500 Index (Standard and Poor’s 500 Index) is a composite of the 500 most actively traded public companies in all ten economic sectors of the U.S. It is maintained by Standard and Poor’s, a division of the Parent company McGraw-Hill.
A Short Sale is a trade in which the investor borrows a security and sells it to another investor in the market.
Security is any financial instrument that represents a financial value.
Recession is generally described as a slowdown of economic growth over a sustained period of time.