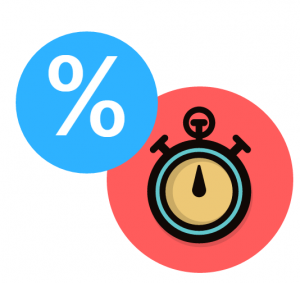
Economists define elasticity as the ratio of the percent change in one variable to the percent change in another valuable. Its purpose is to measure how one variable responds to changes in another variable.
Duration measures the percentage change in the price of a bond (or value of a bond portfolio) due to a change in market interest rates (also known as the yield).
Return on Equity (ROE) is one of the most important pieces of data that investors and creditors use to evaluate a company’s potential to grow and profitability. Dupont Analysis breaks the ROE into several different components in order to analyze where the returns are coming from.
Depreciation refers to the gradual and permanent decrease in value of the assets (referred to as a depreciatable asset) of a firm, nation or individual over its lifetime.
A basic material used in manufacturing or commerce that is interchangeable with other the same commodities coming from a different source. The quality of a specific commodity may differ slightly, but it is essentially uniform across producers. When they are traded on an exchange, commodities must also meet specified minimum standards, also known as a basis grade. Typical types of commodities are corn, gold, silver, steel, etc.
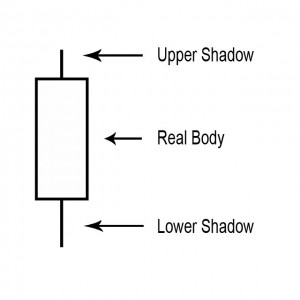
A point on a candle stick chart representing a specific time period (a day, an hour, a minute, etc) in which the underlying stock price has moved. Candlesticks will have a body and usually two wicks – one on each end.
The fee charged by a broker or investment advisor in exchange for investment advice and/or handling the purchase or sale of a security. Commissions vary from brokerage to brokerage.
Earning estimates are an estimate of forecasted earnings and they provide one strong measure of potential future performance and are a mainstay of stock investing research!
A CD or Certificate of Deposit is one of the safest and liquid forms of investment available. Insured by the FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation), CDs are a type of interest earning deposit account.
The buy and hold strategy is essentially just what it sounds like: Purchase stocks and then hold them for an extended period of time. The underlying assumption for the buy and hold strategy is that stocks tend to go up in price over extended periods of time.
The U.S. Dollar has lost more than 30 percent of its value relative to other world currencies. Shorting the U.S. dollar and buying other world currency ETFs is one way to make money from this trend.
A national government that owes money to international financial institutions such as the World Bank, foreign governments, or to foreign lenders.
The Arms Index is a technical analysis indicator that compares advancing and declining stock issues and trading volume as an indicator of overall market sentiment.
Absolute Breadth Index is a market indicator used to determine volatility levels in the market without factoring in price direction.
Advance/Decline Index is a technical analysis tool that represents the total difference between the number of advancing and declining security prices. This index is considered one of the best indicators of market movements as a whole.
A corporation is an entity that abides by specific legal requirements that sets it apart as having a legal existence, as an entity separate and distinct from its stockholders (owners).
A plan offered by a corporation that allows investors to reinvest their cash dividends by purchasing additional shares or fractional shares on the dividend payment date.
Technical Analysis is the use of technical indicator to predict which direction the stock price will move in the future. Technical indicators use past stock prices to calculate their value.
Blue Sky Laws are state regulations governing the sale of securities and mutual funds.
An investment service that allows individuals to purchase a stock directly from a company or through a transfer agent. Not all companies offer DSPPs and the plans often have restrictions on when an individual can purchase shares.
Falling Knife is a phrase used for a stock where the price has dropped significantly in a short period of time. A falling knife security can rebound, or it can lose all of its value where the shares become worthless. Trying to catch a “falling knife” right as it rebounds is dangerous!
An order to buy or sell a stock at a fixed price. This order is active until 1) the trade is executed, 2) the investor decides to cancel it or 3) a specified time period elapses.
Decreasing the long-run average and marginal costs that come from an increase in the size of a factory or plant. Economics of scale can be from the inner workings of an organization. This would include the lower cost from adding technology and better organization.
A 403(b) is an alternative retirement plan to a 401(k) plan offered by non-profit organizations, rather than corporations.
When a company offers to trade one security in return for another security.
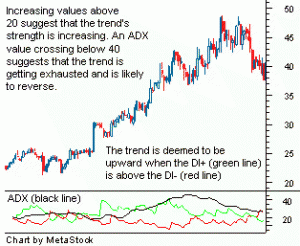
ADX is an indicator used in technical analysis as an objective value for the strength of trend.
If you perform four or more day trades in a 5 day period you may get flagged by the SEC as a “Pattern Day Trader.” This can cause you to lose your margin account status until you deposit enough cash to have $25,000 or more in your account. Many beginning traders have been bitten by this rule!
A trading term called a dead cat bounce is used to when a stock is in a severe decline and has a sharp bounce off the lows. It occurs due to the huge amount of short interest in the market. This bounce will be short lived and followed up by heavy selling which will break the prior price low.
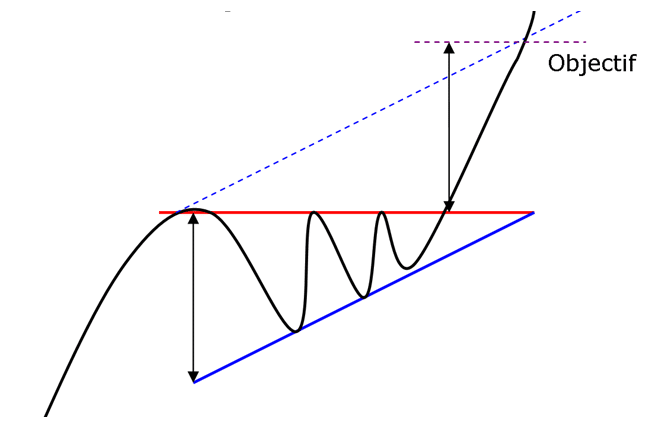
The ascending triangle is a bullish continuation pattern. This pattern is made by two converging lines. The first line is an upward slant which is the support and the other is a horizontal resistance line.
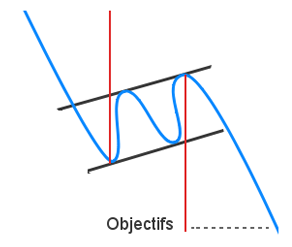
An ascending flag is a continuation pattern formed by two straight upward parallel lines which are shaped like a rectangle. It is adjusted in the direction of the trend that it consolidates.
Charting Software is an analytical, computer-based tool used to help equity (stock) traders with trading analysis by charting the price stock price for various time periods along with various indicators. Equity charting software packages are used by many traders to determine the direction on any given stock price.
Bear ETFs short stocks to achieve their goals. Bear ETFs show gains when the underlying stocks loose value. Bull ETFs use long positions and show gains when the underlying stocks show gains.
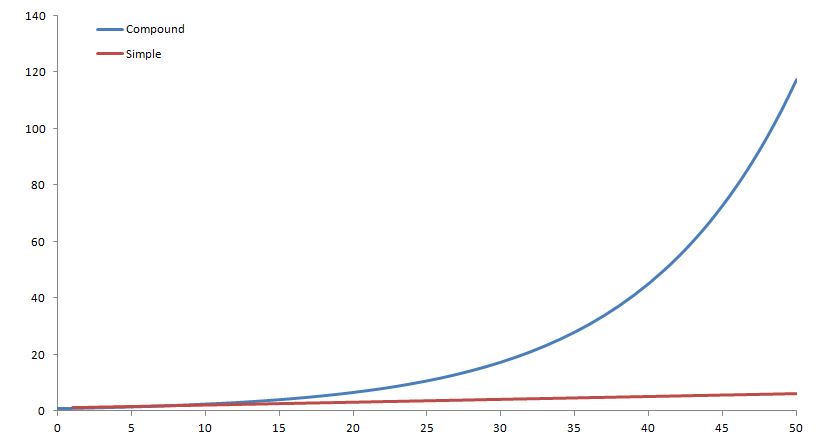
Compound Interest is an extremely important concept in any level of finance. Compound interest can make an enormous difference in the return you get from your investments. As we know, simple interest is the act of earning interest on an investment.
Expiration types determine how long an order will stay open without filling. Your order type is very important for limit orders, but understanding them can also remove a lot of confusion for market orders.
Asset Turnover Ratio is the amount of sales generated for every dollar’s worth of assets.
Day traders buy and sell the same stock (or other investment type) within a single trading day. Day trading has become a very popular way to make money, but it requires dedication and high volumes of cash.
A closed-end fund is a publicly traded investment company that raises a fixed amount of capital through an initial public offering (IPO). The fund is then structured, listed and traded like a stock on a stock exchange.
Covered calls are options strategies by which investors retain a long position in an asset and write or sell a call options on an identical in an effort to produce an increased income from the asset.
The Cash Flow Statement is one of the four financial statements required by the SEC based on the U.S. GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles). This statement presents where the cash and its equivalents are coming from and where they are being allocated.
Dollar Cost Averaging is the method of purchasing a fixed dollar amount of one particular investment at regular period of times, regardless of the share price.
Fundamental analysis is the process of looking at the basic or fundamental financial level of a business, especially sales, earnings, growth potential, assets, debt, management, products, and competition.
Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) is a method used by investors to prioritize what stocks to invest in, given their limited cash.
Buying on margin is borrowing money from a broker to purchase stock.
Cash Flow Per Share is a ratio of the cash generated divided by the number of outstanding shares.
Form 10-Q, is also known as a 10-Q or 10Q, is a quarterly report mandated by the United States federal Securities and Exchange Commission, to be filed by publicly traded corporations.
The price, aka “the ask”, is the lowest price that a seller is willing to accept for a security.
When you are selling your shares of a security, the bid price is what the buyer is willing to pay for your shares.
A Dividend Yield is a financial ratio that shows how much a company pays out in dividends each year relative to its share price. In the absence of any capital gains, the dividend yield is the return on investment for a stock. The formula is Annual Dividends Per Share divided by Price Per Share.
Dividends are payments made by a corporation to its shareholder members. It is the portion of corporate profits paid out to stockholders. When a corporation earns a profit or surplus, that money can be put to two uses: it can either be re-invested in the business (called retained earnings), or it can be distributed to shareholders. There are two ways to distribute cash to shareholders: share repurchases or dividends. Many corporations retain a portion of their earnings and pay the remainder as a dividend.
Common stock is a form of corporate equity ownership, a type of security. The terms “voting share” or “ordinary share” are also used in other parts of the world; common stock being primarily used in the United States. It is called “common” to distinguish it from preferred stock.