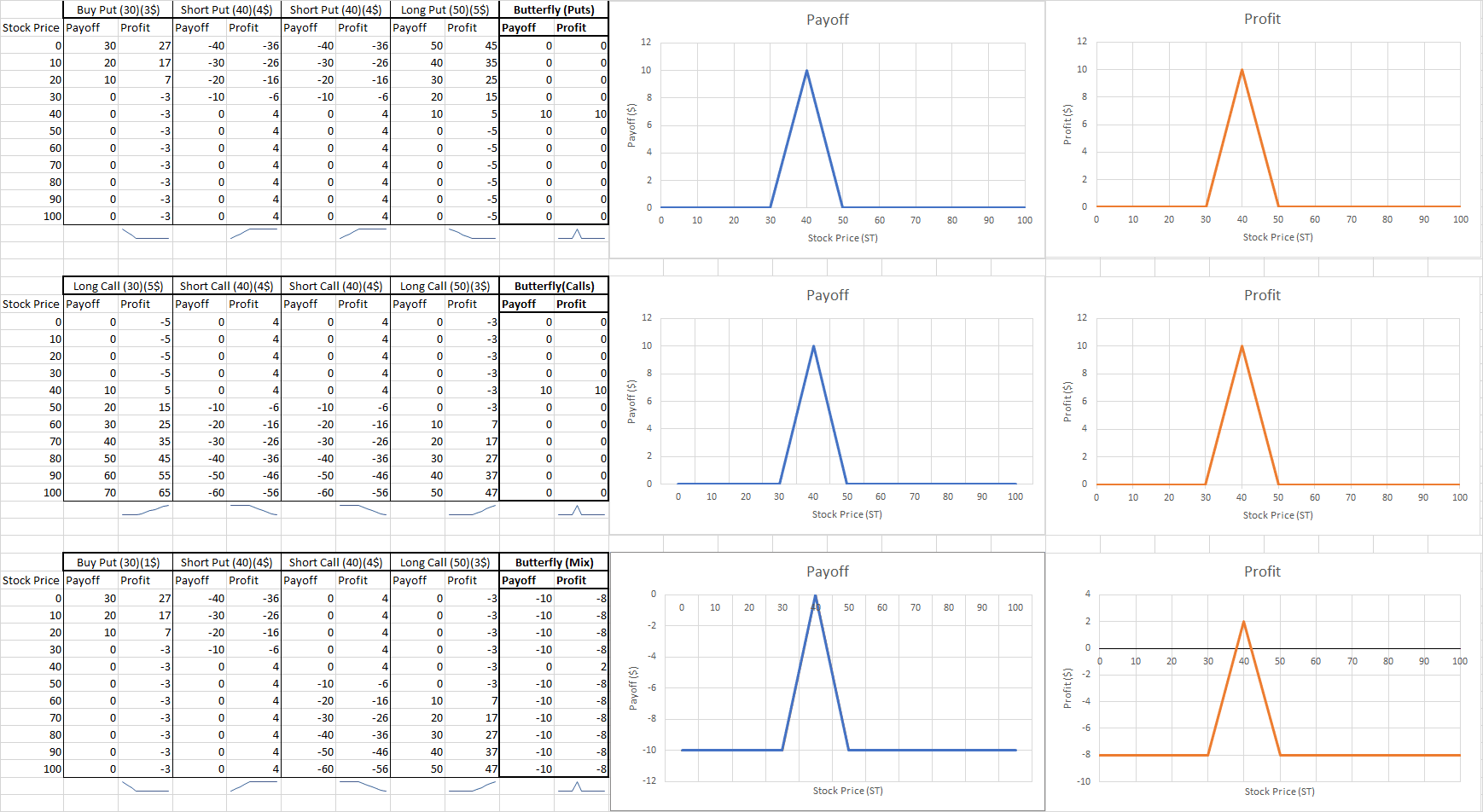
A butterfly is a volatility bet that the trader can implement to protect against large fluctuations, or to gain on volatility.
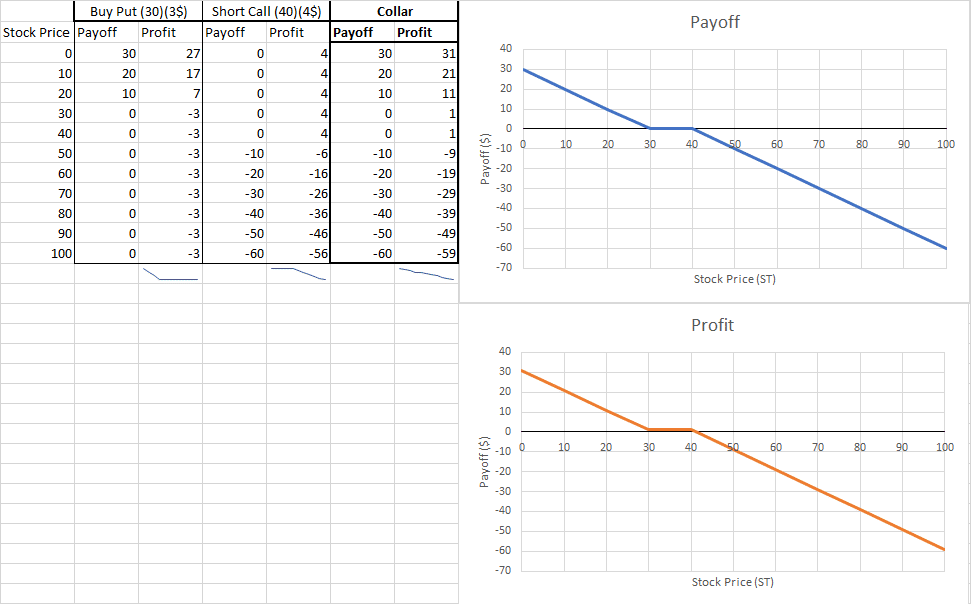
A bullish collar is a protection strategy where you simultaneously buy a call at strike price 1 and sell a put at strike price 2. This strategy is for investors who has a bullish perception on the underlying asset. We can also create a “bearish” collar by simultaneously buying a put at strike price 1 and selling a call at strike price 2.
A box spread is an option strategy that is created by combining the components of the bull spread and the bear spread. In theory, a box spread should always have a zero profit and zero loss, but some investors use them if they see that current options prices aren’t fully “priced in”. In many cases, the commissions charged for the trades needed for this spread will be greater than the profit.
A bear spread is a strategy where you simultaneously buy a call option at Strike Price 1 (some amount higher than the current market rate), and sell a call option at Strike Price 2 (some amount lower than the current market right). This is used if the trader thinks the price of the stock will go down, but not by much. It limits both the risk and reward.
A bull spread is a strategy where you simultaneously buy a long call at Strike Price 1, and sell a call for Strike Price 2 (some higher amount). Use this strategy if you think that a stock’s price will go up above your Point 1, but not as high as your Point 2.
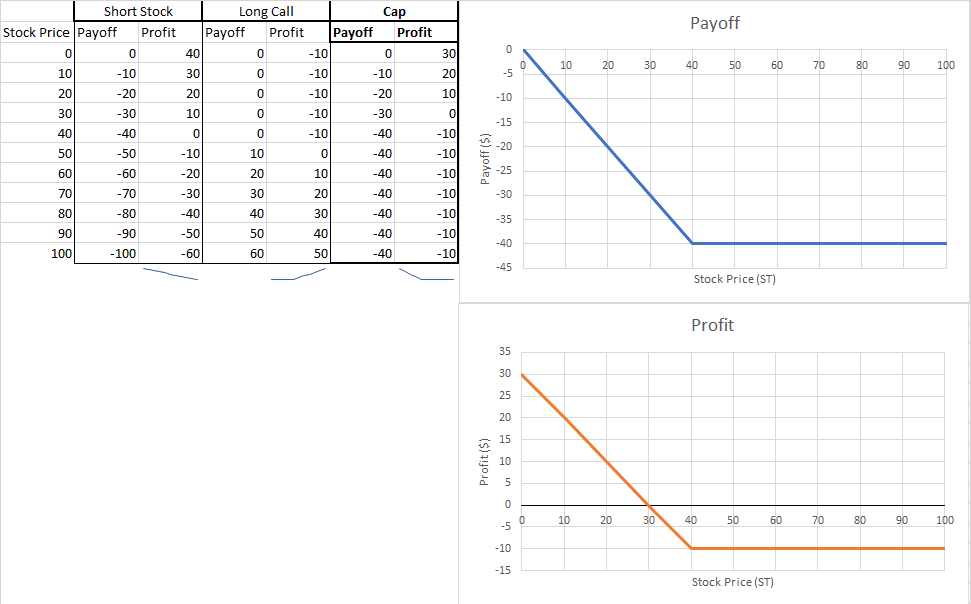
A cap is an options protection strategy where you simultaneously have a short position on a stock and a long call for the same underlying asset. Adding a long call to your open position means that you have the right to cover your short at the strike price.
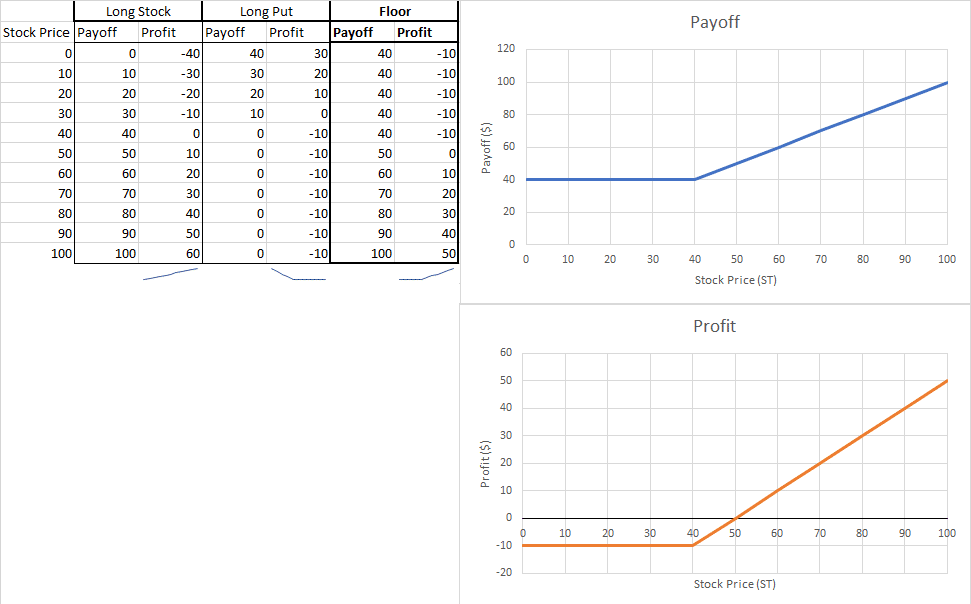
A floor is an options insurance strategy where you simultaneously have a long open position on a stock and a long put for the same underlying asset. Adding a long put to your open position means that if the stock’s price starts to fall, you still have the right to sell it off at the price specified by your option.
A covered put is an options insurance strategy where you simultaneously have a short open position on a stock and sell a put option for the same underlying option. This means you’re shorting a stock, but give someone else the right to sell you that stock at certain price in the future. You would use this if you were certain a stock’s price wasn’t going to go up, but you weren’t sure if would go down either – so you make a bit more money if the price doesn’t change.
A covered call is an options insurance strategy where you simultaneously own a stock and sell a call option for the same symbol (usually for a higher price than what you paid for it). This gives someone else the right (but not obligation) to buy your stock from you later at a specific price. If the underlying stock’s price goes up, the buyer will exercise the option and buy the shares. If the price goes down, the seller of the option keeps both the stocks and the price of the options.
A short call means you sell someone the right to buy a specific stock from you in the future at a certain price. If the stock’s price goes down, they won’t exercise their option, so your profit is the price you sold the contract for.
In the world of trading, owing a long call means that you have a contract that gives you the right to buy the underlying asset at a specific price, before a maturity date.
Brokerages exist to allow individuals to make investments into the larger market. In other words, they connect individuals to the markets as a whole
Future Options are exactly what their name implies – an option on a futures contract.
An Entrepreneur is someone who takes a risk to start a new business. Nearly every business that exists (apart those created as spin-offs of other businesses, or by government intervention) was started by one or several entrepreneurs, who took a risk to launch a new company.
In Economics, an “Externality” is a benefit or cost that is not reflected in the price of a good or service. They can be positive or negative.
A “Contract” is a legally binding agreement between two parties (people, companies, or both). Having a contract means that if one party does not keep their word, the other can sue them in court to either force them to fulfill their side of the agreement, or pay back compensation.
When someone talks about banking, they generally group together Banks, Credit Unions, and Savings and Loans all in one – but their differences can have a big impact on the services you get!
Financial Records are what you use to have an easy way to tell where all your money and assets are, and exactly how much you have, at any given time. Most people’s financial records will not look the same as anyone else’s, because each person has unique ways of organizing their information to make it most accessible for him- or herself.
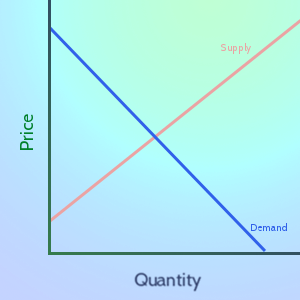
In Economics, “Demand” is the relationship between prices and how much people want to buy a good or service.
There are many different economic systems that try to result in more equality or faster growth. The structure of a country’s economy has a lot to do with the country’s politics and the values of its population. However, the economy of every country also changes over time, and how it falls between these broad categories will often change with it.
The Federal Reserve Bank, or the “Fed”, is the central banking system of the United States. It serves as the primary regulator of the US dollar, as well as the “lender of last resort” for other banks.
Cottage Industry, or the “Putting Out System”, is a production system of producing goods that relies on producing goods, or parts of goods, by craftsmen at home, or small workshops, instead of large factories. Historically the cottage industry was the major production system for most of human history until the Industrial Revolution.
Understanding what it means to build a diversified portfolio is one of the first concepts a new investor needs to understand. When talking about stocks, diversification means to make sure you don’t “put all of your eggs in one basket.”
“ETF” stands for “Exchange Traded Fund”, which is exactly how it sounds; they are like mutual funds in many ways, but they trade on a normal stock exchange like a stock, with their value being determined both by the value of the underlying assets and the value of the ETF itself.
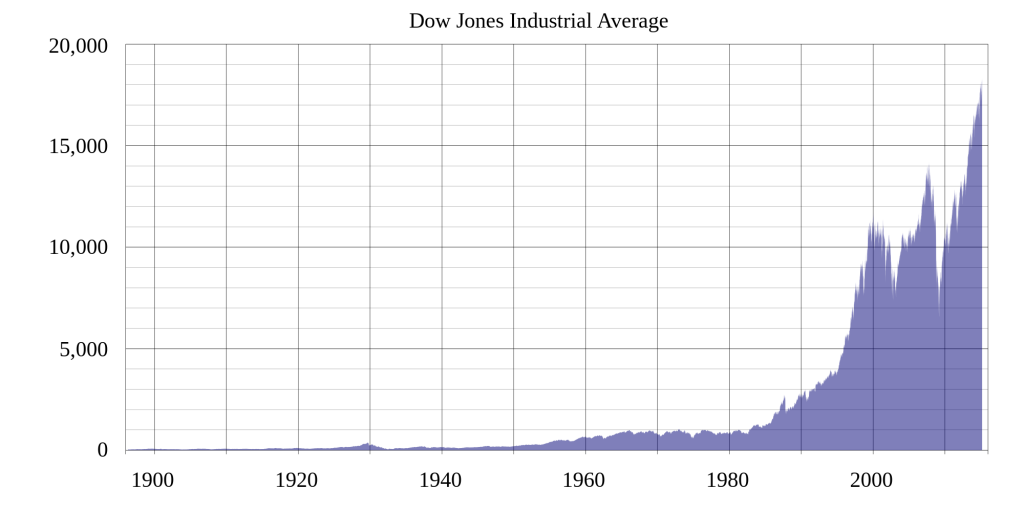
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, more frequently know simply as the Dow or the Dow Jones, is a stock market index made up of 30 of the largest publicly-owned companies based in the United States. It is a price weighted index meaning that the index’s price is an average of the price of the 30 stocks that make it up. Though it is price weighted, this does not mean that every time there is split the index is completely changed, as they have factors to keep the value of the index consistent.
The balance sheet is a financial snapshot of the firm on a specific date – specifically their assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity
Fibonacci Arcs and retracements are used as a technical indicator to determine support and resistance. As with most indicators it can be used to see if a breakout has occurred or if a reversal is likely to happen.
Forex or (FX) is the term used for the world’s currency market. It comes from the words “Foreign Exchange”.
Bonds are essentially a much more formal I.O.U (I owe you) used to borrow money. You buy the bond in return to interest over a given period of time.
An asset is anything that has monetary value and can be sold. Assets can be anything from a pencil (though it is not worth much) to a skyscraper to things like Stocks and ETFs.
“Asset Allocation” is how you have divided up your investments across different assets. You can have all your assets in one place, or you can use diversification to spread them around to reduce risk.
A “Good-Till-Day” order is simply one that will cancel at the end of the trading day if it does not fill.
Fixed Income represents a distinct asset class, typically of corporate and treasury bonds. This type of investment doesn’t usually have a high return, but gives a consistent “fixed” return over time
The Black-Scholes formula is the most popular ways to calculate the “true” price of an option.
Arbitrage is the simultaneous purchase of a security on one stock market and the sale of the same security on another stock market at prices which yield a profit.
Gross National Product (GNP) is the value of all goods and services produced by a country’s residents.
Free Cash flow is the cash available to all the capital providers of a company. There are two types of free cash flows: 1) Cash flow available to pay out to all capital providers and 2) Free Cash Flow to Equity (FCFE).
The Form-8K is a SEC-mandated report filed by public companies to report unexpected events or transactions that are material in nature, and thus have an impact on the share prices of the company.
The earnings reports released by companies can be invaluable in providing relevant, timely, and high-quality information to help investors make the most informed decisions possible.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) is a valuation technique or model that discounts the future cash flows of a business, entity, or asset for the purposes of determining its value.
Covariance is a statistical measure of the extent that 2 variables move together relative to their respective mean (or average) values.
Correlation is a measure of the strength of linear association between two variables or more variables of interest. We can measure the degree and direction of their linear association using correlation analysis. Read this article to learn more!
Comprehensive insurance to a form of insurance policy which includes a broad range of coverage or protection. This article discuss the types, features, and advantages of comprehensive insurance.
The Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME Group) is a publicly-traded derivatives-based exchange (NasdaqGS: CME), and is currently the largest futures exchange in the world in terms of number of contracts outstanding (or open interest).
The Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT) is a publicly-traded exchange (NYSE: BOT) that specializes in futures and options trading. It is highly active in markets such as agriculture, energy, equities, and US Treasuries, providing an important risk-management function for thousands of its CBOT members.
Cash Conversion Cycle is defined as the length of time (in days) needed to transform inventory purchases into actual cash receipts. It takes into consideration the company’s time commitment towards collecting receivables and paying its suppliers, and is an important measure of a company’s internal liquidity.
Capital funding is the provision of monetary resources or capital for productive uses. Capital provided by investors or other parties is used by various entities such as governments, companies, organizations, and individuals in order to fund their functions and operations.
Account Receivables Management refers to the set of policies, procedures, and practices employed by a company with respect to managing sales offered on credit. If efficient, receivables management can lead to good sales growth, healthy cash flows, profitability, and stable operating cycles.
Account Payables Management refers to the set of policies, procedures, and practices employed by a company with respect to managing its trade credit purchases. It is an important working capital amount that can enhance a company’s short-term cash flow position.
The Expected Return is a weighted-average outcome used by portfolio managers and investors to calculate the value of an individual stock, or an entire stock portfolio.