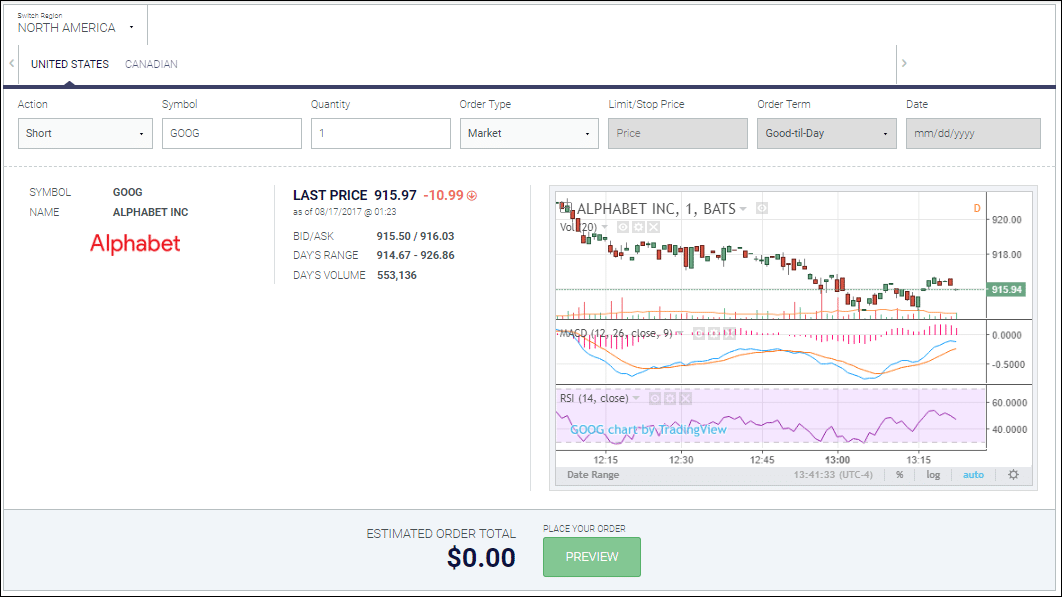
A short stock is an expression used when you sold shares of a company that you did not own beforehand, and is described in more detail in this post!
A Strangle is a volatility bet where you simultaneously long a put at Strike Price 2 and long a put at Strike Price 1, betting the stock price will make a big movement in either direction. This is similar to a Straddle, but the trader shorts the stocks instead of buying them (but the profit is basically the same)
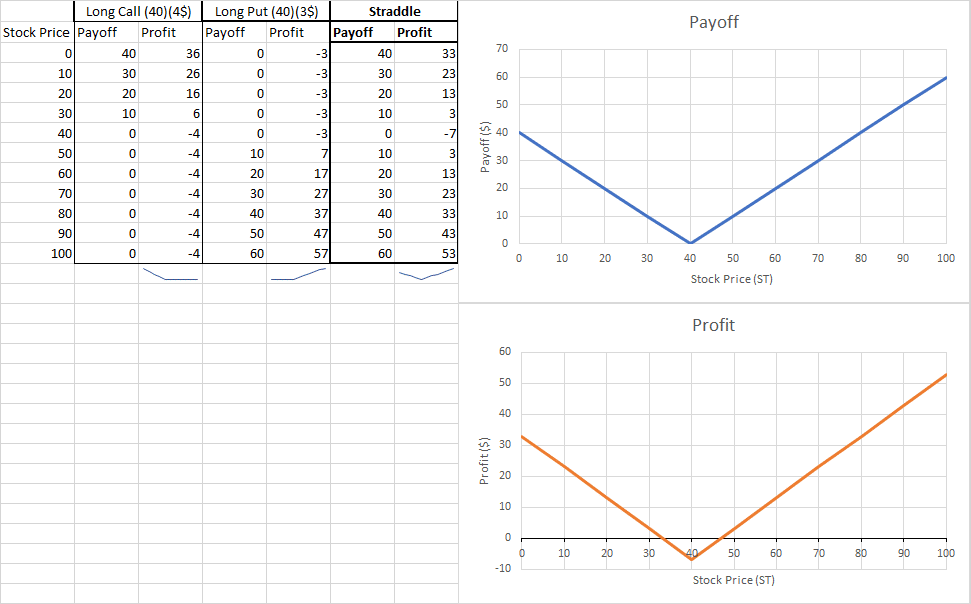
Straddles an option strategy that profits with volatility. You simultaneously buy long a call at Strike Price 1 and long a put at Strike Price 1. This creates a triangular shaped payoff and profit graph where the reward is based on the volatility of the stock – you’ll make a profit if the stock’s price makes a BIG move in either direction, but take a loss if it doesn’t move much.
A ratio strategy is an option strategy that is created by having X amount of call options at Strike Price 1 and shorting Y amount of call options at Strike Price 2. This strategy is used when the investor thinks the price won’t move much, but they want to get a bigger profit based on a slight movement up or down.
A short call is a term used when you sell a call option for an underlying asset. If you use this type of option, you’re selling someone else the right to buy a stock from you at a certain price in the future. If the stock’s price goes down, you keep the money you made by selling the option. If the stock’s price goes up, you are required to sell the stock at the agreed upon price, taking a loss.
A short put, the opposite of a short call, is the term used when you sell a put option for an underlying asset. You make a flat profit if the stock’s price goes up, but lose money if the price goes down
A “Long Put” means buying the right to sell a stock at a certain price at a certain date in the future. You would buy a “Long Put” if you expected the stock’s price to go down.
You “Short a stock” by borrowing a stock from your broker, then immediately selling it. Later, you buy the stock back on the market, and return it to your broker. You make a profit if the stock’s price dropped between when you sold it and when you bought it back.
A long stock is an expression used when you own shares of a company. It represents a claim on the company’s assets and earnings.
Solvency is the possession of assets in excess of liabilities, or more simply put, the ability for one to pay their debts. People and organizations who are not “Solvent” face bankruptcy
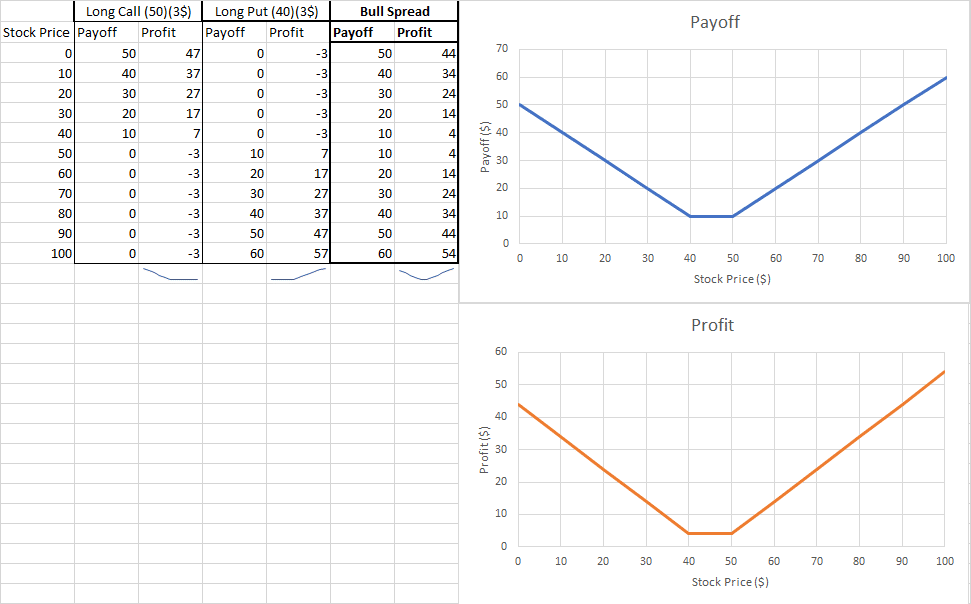
Options Spreads are option trading strategies which make use of combinations of buying and selling call and put options of the same or varying strike prices and expiration dates to achieve specific objectives (hedging, arbitrage, etc.).
“Price Controls” are artificial limits that are put on prices. If the limit is put in place to prevent prices from getting too high, they are called Ceilings. If they are in place to prevent the price from getting too low, they are called “Floors”.
Scarcity refers to the fact that resources are finite – people and organizations need to allocate their finite resources between their infinite wants.
“Specialization” is when a labor force begins to divide total production, leading to a rise of experts or specialists. This is called the Division of Labor, and it typically results in much higher productivity of labor.
“Opportunity Cost” is what needs to be given up to get something. This is different from an item’s price – it refers to what you give up in order to get something. The opportunity cost for going to school is that you can’t stay home and nap. The opportunity cost of staying home to nap is not getting your diploma!
A Spending Plan is a plan of what you will spend each month, and includes fixed and variable spending. They are used similarly to a budget, but many find them to be more flexible
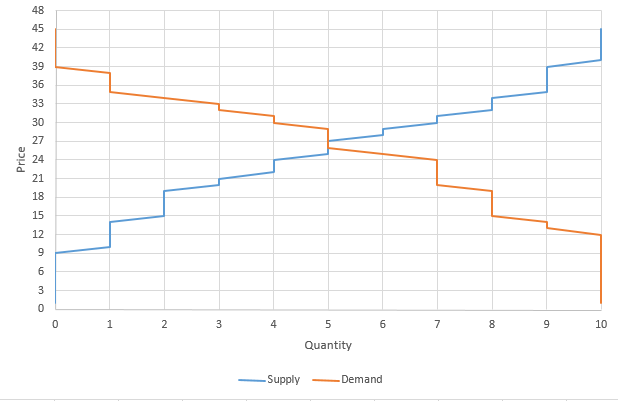
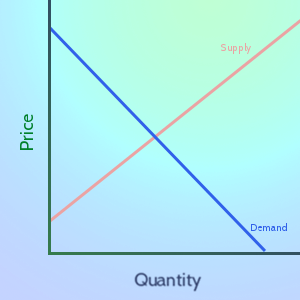
The stock market is the perfect place to see Supply and Demand in action! Many buyers and many sellers meet to trade – with the “market equilibrium” moving in real-time based on new information
In Economics, “Supply” means the relationship between prices and production. In general, the higher the market price of a good or service is, the more producers are willing to sell of it.
The Reserve Requirement is how much of all deposits that a bank is required to keep “on hand”, meaning in its vaults, or on deposit at the Federal Reserve Bank (in the United States).
The stock market crash of 1929 was a massive crash in stock prices on the New York Stock Exchange, and marks the largest financial crash in the United States.
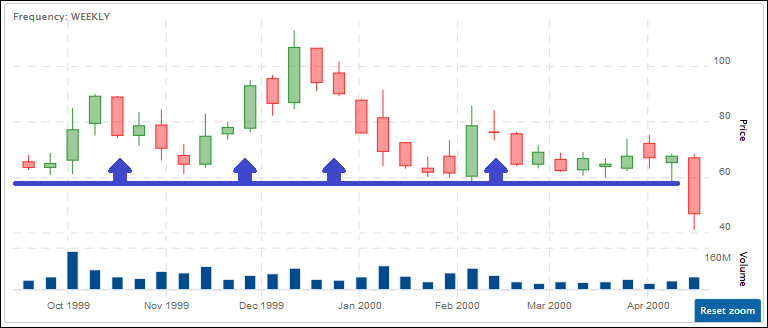
“OHLC” stands for “Open, High, Low, Close”, and this is a chart designed to help illustrate the movement of a stock’s price over time (typically a trading day, hour, or minute).
Spot and Futures contracts are a standardized, transferable legal agreement to make or take delivery of a specified amount of a certain commodity, currency, or an asset at the current date. The price is determined when the agreement is made.
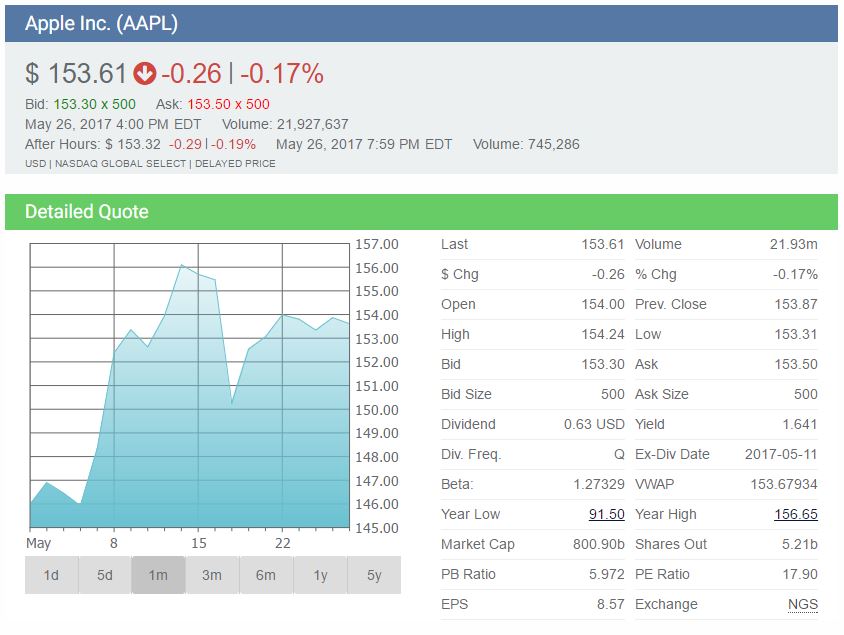
A stock quote represents the last price at which a seller and a buyer of a stock agreed on a price to make the trade. Stock quotes also contain information about the volume, high and low prices of the day and year, and more.
A “Ticker Symbol” is a unique one to five letter code used by the stock exchanges to identify a company.
The New York Stock Exchange (or NYSE) is the largest stock exchange in the world, where buyers and sellers come to trade U.S. stocks!
Stocks are a share of ownership of a company. If you own a stock, you are involved in some of its management decisions, and you are entitled to some of the company’s profits.
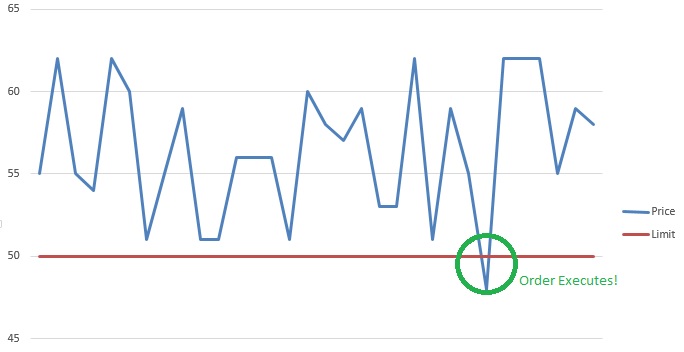
A Stop (or stop loss) order and Limit order are orders that try to execute when a certain price threshold is reached. These orders are mirrors of each other; they have the same mechanics, but have opposite triggers.
Trailing Orders are an order type that allows to set a moving stop or limit target price.
Your “Risk Level” is how much risk you are willing to accept to get a certain level of reward; riskier stocks are both the ones that can lose the most or gain the most over time.
Open Interest is the total number of options or futures contracts that are “open”, meaning currently owned by an investor and not yet expired.
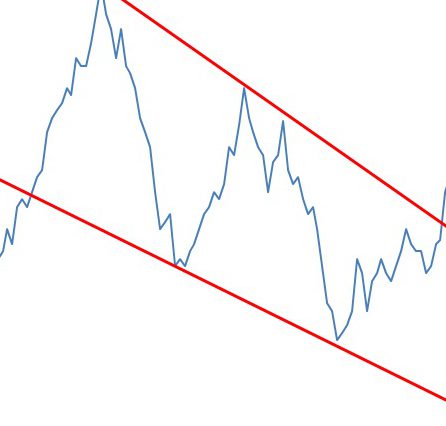
A pullback is a technical analysis term used frequently when a stock “pulls” back to a resistance and/or support line, usually after a breakout has occurred.
The Sharpe Ratio is an important tool for evaluating a stock, or a portfolio, based on how risky it is to get a higher return. You can use it to determine how consistent the returns of a stock or portfolio are, so you can determine if the returns are stemming more from wise investing, or “getting lucky”.
There are also thousands of companies that want to sell shares to the general public, but are not able to sell on exchanges like NASDAQ, or the NYSE. Therefore, other exchanges exist to allow these companies to sell public shares. Stock traded on these “Over The Counter” exchanges are known as OTC stocks.
A price ceiling is a government-mandated limit on the price that can be charged for a given product, such as a utility or electricity. The intended purpose of a price ceiling is to protect the consumers from conditions that would make a vital product from being financially unattainable for consumers.
A “Poison Pill” is a way to give shareholders more time to evaluate a hostile takeover bid and to give management the opportunity to make better informed business decisions. It was created in the 1980’s, a period rife with hostile takeovers and corporate raids.
An oligopoly is characterized by a small number of sellers who dominate an entire market. All of the firms who partake in an oligopoly are considered to be very large in terms of profit, size and client base.
Straight line depreciation is the most commonly used and simplest form of depreciation.
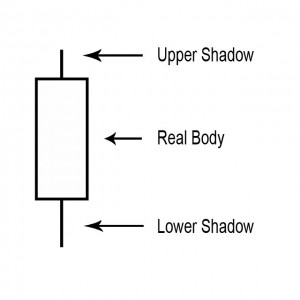
A shadow is the small line (like a candle wick) found at the top or bottom of an individual candle in a candlestick chart.
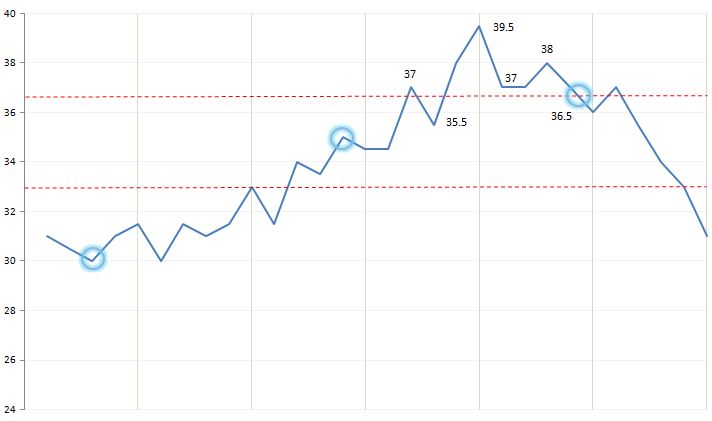
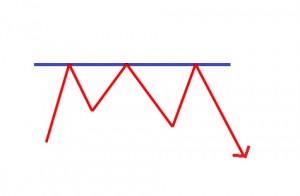
The Resistance Line is a point or range in a chart that caps an increase in the price of a stock or index over a period of time.
The price-to-sales ratios (Price/Sales or P/S) take the company’s market capitalization (the number of shares multiplied by the share price) and divide it by the company’s total sales over the past 12 months. The lower the ratio, the more attractive the investment.
Stagflation is high inflation and high unemployment are occurring simultaneously.
This post describes, Return on Equity (ROE), which is used to measure how much profit a company is able to generate from the money invested by shareholders.
Price/Earnings To Growth, is a valuation metric for determining the relative trade-off between the price of a stock, the earnings generated per share (EPS), and the company’s expected future growth. It can be useful when looking at the future earning growth.
Stock volatility information can be used in many different ways but here is a quick and easy bit of stock volatility information that you can begin using today.
Small cap stock investing is volatile. So, why risk your money by investing in what is typically considered risky business?
Market Risk, aka Systemic Risk, which is a measure of how much of a loss an investor is facing while trading.
Everywhere you turn there is another proprietary stock market timing system being sold. This is usually a computer program that tries to analyze real-time data for split-second trade decisions
The offer price, or the Bid price is what an investor is willing to pay for an investment. It is only an offer and will not be accepted if the seller is not willing to let go at the offer price.
The difference between the ask price and the sell price is called the “spread” and it is kept by the broker.
If you are brand new to investing then take time to understand what you are reading when viewing a Stock Exchange Symbol and learn Stock Market Investing Basics.